Data transmission
1. Introduction
Data transmission means to move information (data) from one place to another.
The most fundamental unit of digital data is the bit. This is a binary digit that has two logic states - a logic 0 or a logic 1.
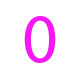 |
|---|
Roll over the image to see the two types of binary bits |
In actual systems, the bit has to be represented by something physical that has two values. For example a copper network cable could use two different voltages, one for binary 1 and the other for binary 0.
The speed of transmission is measured as the bit rate. This is the number of bits transmitted per second.
For example fibre optic broadband may have a bit rate of 64 Mbit/s whilst a copper cable version may only manage 15 Mbit/s. Streaming high definition (HD) TV shows and films need about 5 Mbit/s.
