3. Packet Switching
Packet switching is an alternative method of sending data across a network.
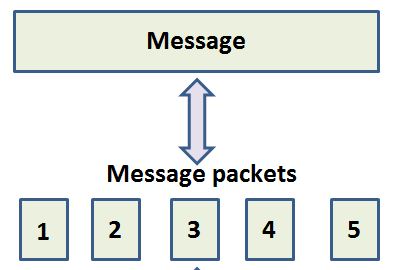
Unlike circuit switching where the whole message is sent in one go, with packet switching the message is broken down into smaller parts (data packets) and these parts are sent individually through the network.
The packets are given a 'packet number' to identify the order they are in.
The packets will travel across the network, usually in different directions, taking the shortest route available.
When the individual packets arrive at their destination they will be reassembled back together in the correct order.
Once all of the packets have safely arrived a message will be sent to the original computer as confirmation.
If a packet is missing or corrupted then the message will instead be sent asking for that particular packet to be resent.
Typical protocols used with packet switching are
- Ethernet
- TCP/IP
We have a separate section on protocols here.
Challenge see if you can find out one extra fact on this topic that we haven't already told you
Click on this link: What is a data packet
